Other Corrosion Protection Systems
There are many other types of corrosion protection systems, such as coating steel with oil, grease, tar, asphalt, polymer coatings or paints, or corrosion resistant materials such as stainless and weathering steel, sacrificial anodes, plating systems and impressed current systems. These are some of the most commonly used corrosion protection materials and systems and are sometimes used in conjunction with hot-dip galvanized steel. Most of these materials rely on barrier protection, while some of them rely on cathodic properties to resist steel corrosion. The most effective system that provides both barrier and cathodic protection is hot-dip galvanizing.
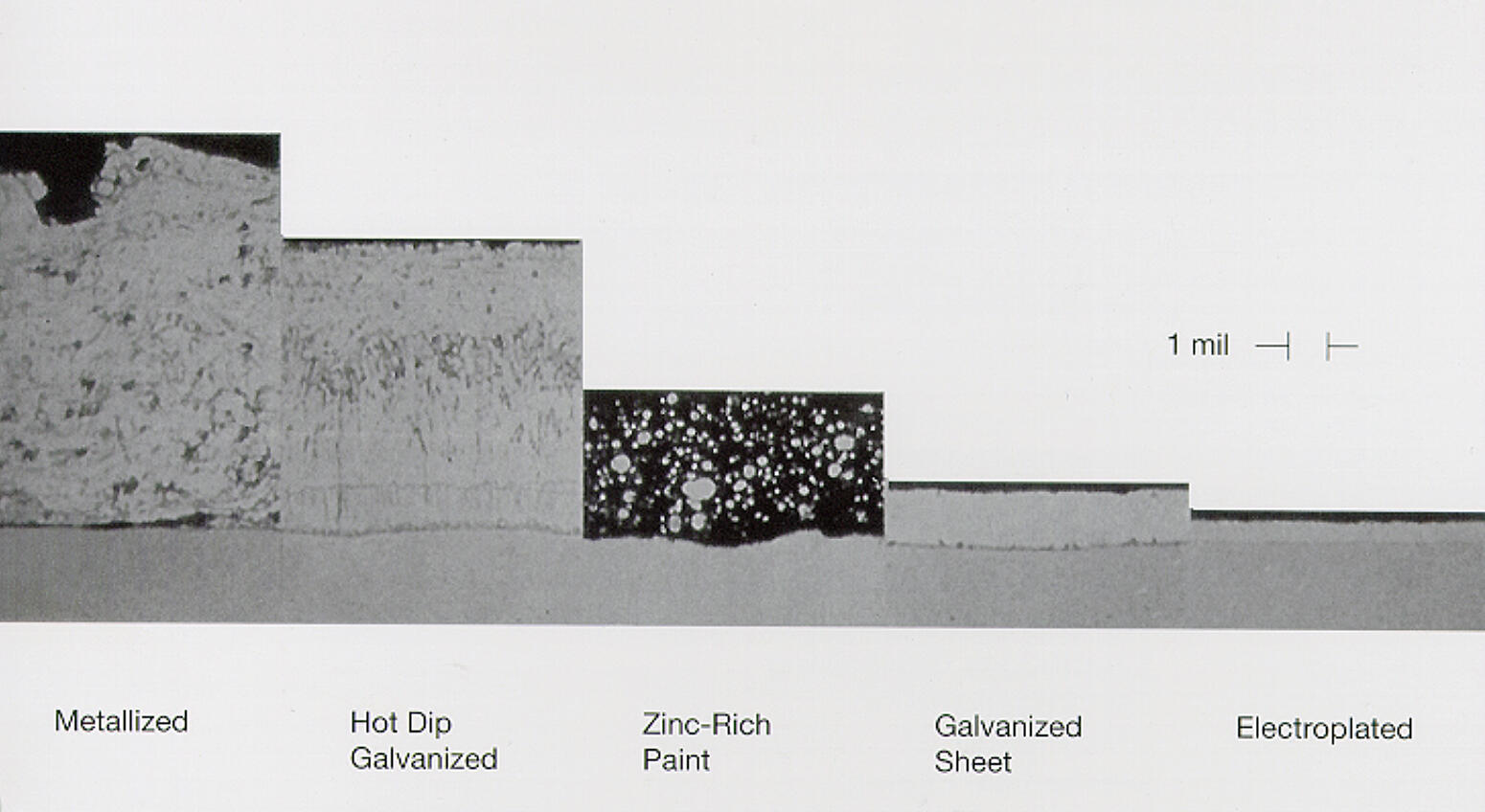
In addition to the systems and materials listed above, there are a wide variety of other zinc coatings used for corrosion protection. Many people use galvanizing to describe all of these coatings, but each has its own unique characteristics and performance. These coatings have several applications based on their properties and respective thicknesses. The corrosion protection offered by a zinc coating is directly linear to the coating thickness. The most commonly used coatings are hot-dip galvanized, metallized, zinc-rich paint, continuous galvanized sheet, and electroplated. The relative thickness for each of these zinc coatings can be seen in the photomicrograph (Figure 8). Below is a brief explanation of each type of zinc coating
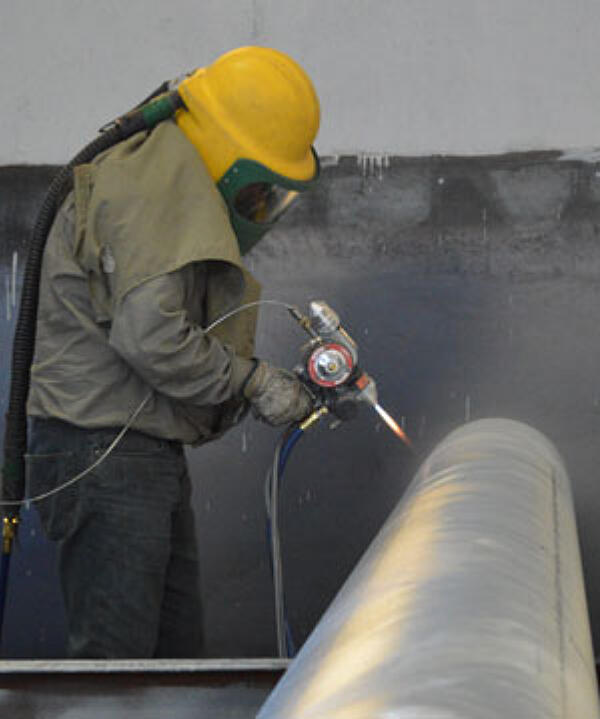

Metallizing
Metallizing is the general name for the technique of spraying a metal coating on the surface of non-metallic or metallic objects. This process is accomplished by feeding zinc in either wire or powder form into a heated gun, where it is melted and sprayed onto the surface to be coated using combustion gases and/or auxiliary compressed air to provide the necessary velocity. The limitations of this process include a difficulty in reaching recesses, cavities, and hollow spaces as well as achieving a uniform coating thickness and the higher cost.
Zinc-Rich Paint
Zinc-rich paint is applied to a clean, dry steel surface by either a brush or spray and contains an organic or inorganic binder. There are a number of zinc-rich paints, as they can contain varying levels of zinc in dry film and binding materials. These coatings will be discussed in more detail later in this course.

Continuous Galvanizing
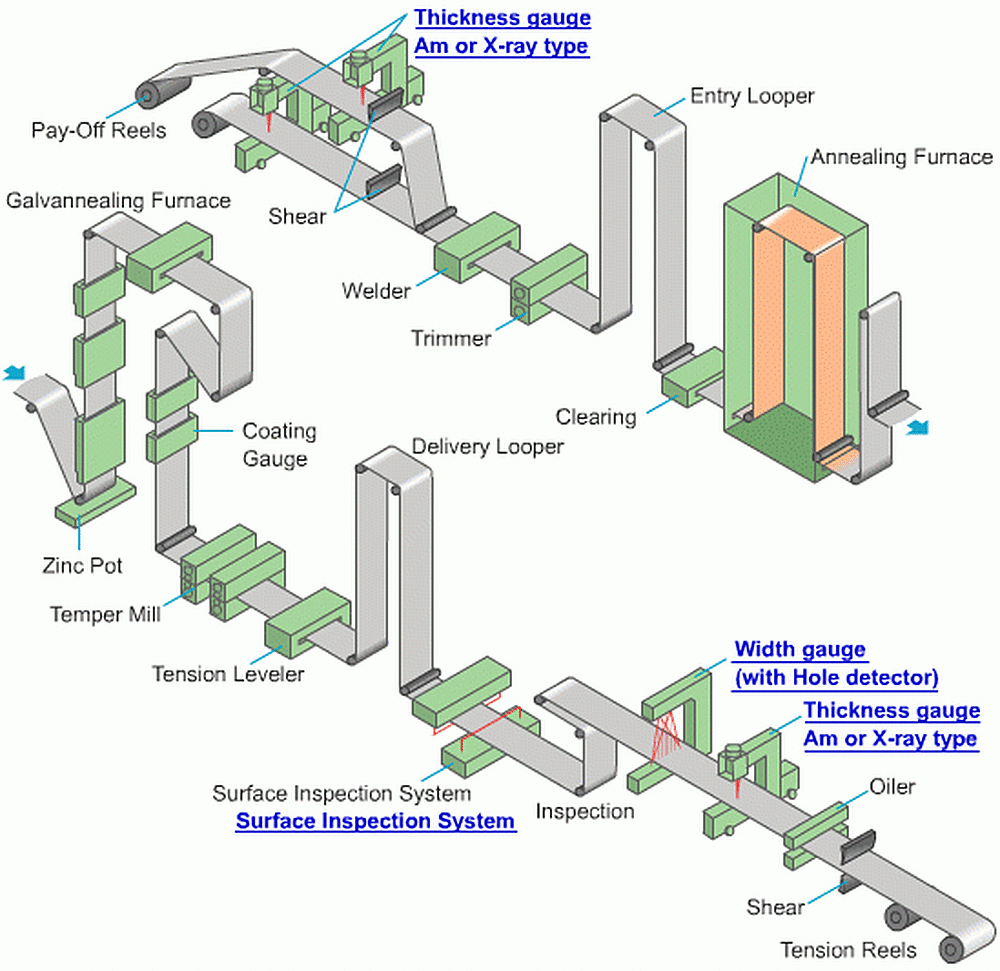
The continuous galvanizing process is a hot-dip process where steel sheet, strip, or wire is cleaned, pickled, and fluxed on a processing line approximately 500 feet (154 m) in length, and running at speeds between 100 to 600 feet per minute (30 to 185 m per minute). In this process, the galvanizing kettle contains a small amount of aluminum, which suppresses the formation of the zinc-iron alloys, resulting in a coating that is mostly pure zinc. A post-galvanizing, in-line heat treatment process known as galvannealing can also be used to produce a fully alloyed coating. Galvannealing is usually ordered by those wanting to paint over the zinc surface because the presence of alloy layers on the steel surface promotes paint adhesion. A photo of a continuous galvanizing plant is seen in Figure 9 and the common plant setup is shown in Figure 10.
Electroplating
The electroplating process, or zinc-plated coating, has a dull gray color, a matte finish, and a thin coating that ranges up to one mil (25 µm) thick. This very thin coating restricts the use of zinc-plated products to indoor exposures. The specification ASTM B633 lists the classes of zinc-plated steel coatings as Fe/Zn 5, Fe/Zn 8, Fe/Zn 12, and Fe/Zn 25, where Fe represents iron and Zn represents zinc, while the number indicates the coating thickness in microns. The main uses for this type of coating include screws, light switch plates, and other small products or fasteners.